Explain Fully Null Hypothesis Sampling Difference and Significant Difference
By Theorem 1 of One Sample Hypothesis Testing for Correlation under certain conditions the test statistic t has the property. The difference between expected versus actual indicates which hypothesis better explains the resulting data from the experiment.

Inquiry Session 2 Goal Setting And Backward Design Every Statistical Test Starts With A Null Data Science Learning Social Science Research Psychology Studies
Experimental design is an efficient method of optimizing the experimental conditions for SPE to maximize the amount of useful information obtained with the minimum number of experiments.

. Putting these elements together we get that. One-tailed hypothesis tests offer the promise of more statistical power compared to an equivalent two-tailed design. Before we continue I need to quickly explain a concept called the null hypothesis.
We now show how to test the value of the slope of the regression line. A two-tailed test also known as a non directional hypothesis is the standard test of significance to determine if there is. In this post I discuss when you.
And by Definition 3 of Regression Analysis and Property 4 of Regression Analysis. Report the data-based odds of the alternative hypothesis to the null hypothesis. A primary difference between bootstrapping and traditional statistics is how they estimate sampling distributions.
While there is some debate about when you can use a one-tailed test the general consensus among statisticians is that you should use two-tailed tests unless you have concrete reasons for using a one-tailed test. P-value is produced by the statistical software and it is a minimal significance level at which we can reject the null hypothesis. The second type of question is a questionhypothesis of difference and will often have the word difference as part of the question.
Report your prior odds and posterior odds prior odds data-based odds of the alternative hypothesis to the null hypothesis. But the hypothesis that m components account for all the variance in p variables is essentially the hypothesis that when the variables are predicted from the components by multiple. When a statistical hypothesis test is run the results either disprove the null hypothesis or they fail to disprove the null hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is a baseline assumption that there is no relationship between two data sets. Statistics is the discipline that concerns the collection organization analysis interpretation and presentation of data. You have substantial latitude about what to emphasize in Chapter 1.
Market efficiency is typically conducted as a test of the random walk hypothesis. It provides a more efficient and complete optimization. If the data-based odds cannot be calculated then use the p-value to report an upper bound on the data-based odds.
Traditional hypothesis testing procedures require equations that estimate sampling distributions using the properties of the sample data the experimental design and a test statistic. This means that when we make a first planned interim look analysis we compare the difference between the conversion rates and reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 000001. The usual null hypothesis would be that the population proportions are equal eg expected frequencies for each color would be N 1C where N is the total number of flies observed and C is.
I find it useful to talk about the economics of crime example Example 11 and the wage example Example 12 so that students see at the outset that econometrics is linked to. 322 Testing for Market Efficiency. As my understanding p-value is the probability that using a given statistical model the statistical summary such as the sample mean difference between two compared groups would be the same as or more extreme than the actual observed results Wikipedia given the null hypothesis is true.
But by Property 1 of Method of Least Squares. The very first research question in this section asking if there is a difference between 1st year and 4th year college students use of Facebook is an example of this type of question. The most commonly conducted test for the random walk is the variance ratio test of Lo and MacKinlay 1988The variance ratio test is based on the property that the variance of.
Any deviation from 10 no matter how small contradicts the null hypothesis. In cases where an experiment is repeated many times a statistical analysis such as a chi-squared test whether. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as all people living in a country or.
A similar argument applies to the hypothesis that a multiple correlation is 10. Bruce Vanstone Tobias Hahn in The Handbook of High Frequency Trading 2015. In applying statistics to a scientific industrial or social problem it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied.
Poole in Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation 2012 21454 Optimization by Experimental Design.
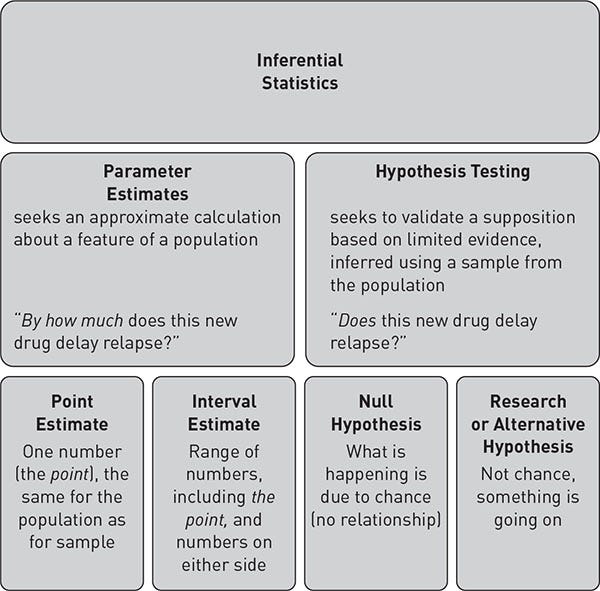
Basic Difference Between Inferential Statistics And Hypothesis Testing By Techguy Medium

The Confusion Matrix Of Accepting Or Rejecting The Null Hypothesis H0 Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "Explain Fully Null Hypothesis Sampling Difference and Significant Difference"
Post a Comment